Marc Dupuis
GéniSim Inc.
3111 Alger St.,
Jonquière, Québec, Canada G7S 2M9
email:
According to many recent aluminium market studies (Merrill Lynch, AME, etc.), if most of the current capacity expansion projects are realized (China, Africa, Canada, etc.), the industry is heading toward a significant production overcapacity in 2005.
In this scenario, older less productive smelters with high production costs will be forced to close permanently their operations. Considering their age and their current power efficiency, this situation places at risk, among others, many of the Indian smelters.
Taking this threat very seriously, the technical leaders of the Indian aluminium smelting industry took advantage of the International Aluminium Electrolysis Seminar - 2002 (ALEL 02, see Figure 1) organized last summer by the Jawaharlal Nehru Aluminum Research Development and Design Centre (JNARDDC, e-mail: jnarddc@nagpur.dot.net.in), to come up with recommendations for an "Indian Aluminium Smelters Roadmap" (see Figure 2).
The main roadmap recommendations are as follow:
| - | Inert anodes/drain cathode/multipolar cell technologies are not the answer to the short term threat faced by our industry |
| - | As electrical power in India is becoming more and more in short supply and the average power consumption of the Indian smelters is very high as compared to world standards, extensive efforts should be made to reduce their power consumption |
| - | Power consumption reduction should be achieved by small increments over a certain period of time, based on projects where improvements can be obtained without any major change in the cell design or operation of the existing plants |
| - | Mathematical modeling is identified as the most efficient way to come up with viable recommendations for design changes aiming at reducing the power consumption of the existing plants |
| - | The JNARDDC is therefore mandated to coordinate the effort of developing and applying mathematical modeling in the most efficient way in order to support the Indian aluminium industry efforts to increase its productivity |
To fulfill its mandate, the JNARDDC a "Centre of Excellence" setup in 1989 in Nagpur (located at the geographical center of India) by the Department of Mines of the Indian government, decided to:
| - | Work in collaboration with international experts in the area of mathematical modeling of aluminium reduction cells as, with this collaboration, it is expected that the time and expense involved in developing customized mathematical models for the Indian smelters by the JNARDDC would be considerably reduced |
| - | Select Dr. Marc Dupuis from GeniSim Inc. Canada to develop thermo-electric models of the cell, either 3D steady-state models using ANSYSŪ commercial finite element code or lump parameters+ dynamic models using Dyna/Marc commercial cell simulator |
| - | Select ANSYS India to give basic local support on the use of ANSYSŪ general purpose finite element code |
| - | Select Dr. Valdis Bojarevics from the University of Greenwich UK to develop MHD cell stability models of the cell using his own code |
As far as GeniSim Inc. involvement is concerned, the following model development projects likely to come up with the JNARDDC have already been identified:
| - | The development of 3D steady-state thermo-electric ANSYSŪ-based cathode side slice models of the Hirakud's smelter HSS cell and the Korba's smelter VSS cell in order to be able to recommend changes in the lining design aiming at reducing the power consumption and increasing the line amperage |
| - | The development of a 3D steady-state thermo-electric ANSYSŪ-based cell side slice model (see Figure 3) of the Angul's smelter prebaked cell in order to be able to recommend changes in the lining design aiming at reducing the power consumption and increasing the line amperage |
| - | The development of Dyna/Marc dynamic models of the Hirakud's smelter HSS cell, the Korba's smelter VSS cell and the Angul's smelter prebaked cell (see Figure 4) in order to be able to analyze different power modulation scenarios |
| - | The development of a 3D dynamic thermo-electric ANSYSŪ-based cathode side slice preheat model of the Hirakud's smelter HSS cell in order to be able to analyze different cell preheat strategies aiming at increasing the cell life |
The threat being faced by the Indian aluminium industry repeats itself worldwide, and it is logical to think that the no-nonsense recommendations of the Indian roadmap to address that threat are equally valid worldwide.
Figure 1: Dr. Marc Dupuis presentation at the ALEL 02 seminar
Figure 2: The Indian Aluminium Smelters Roadmap panel
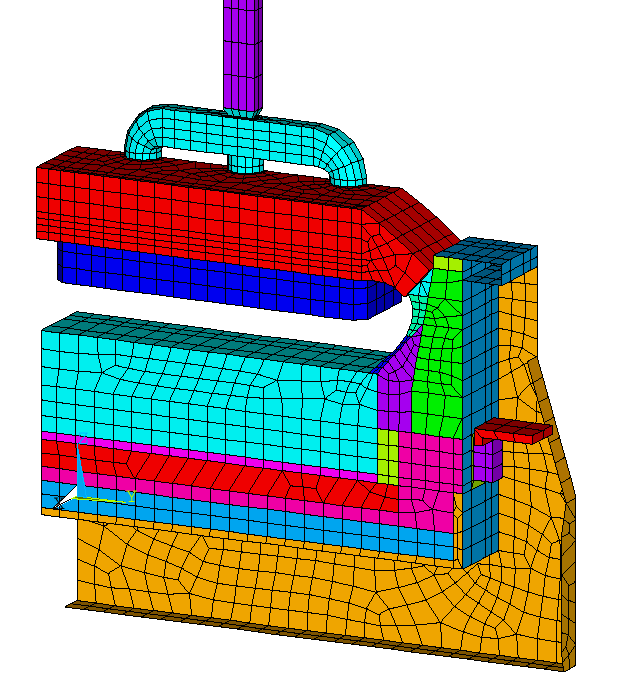
Figure 3: Example of 3D thermo-electric ANSYSŪ-based cell side slice model
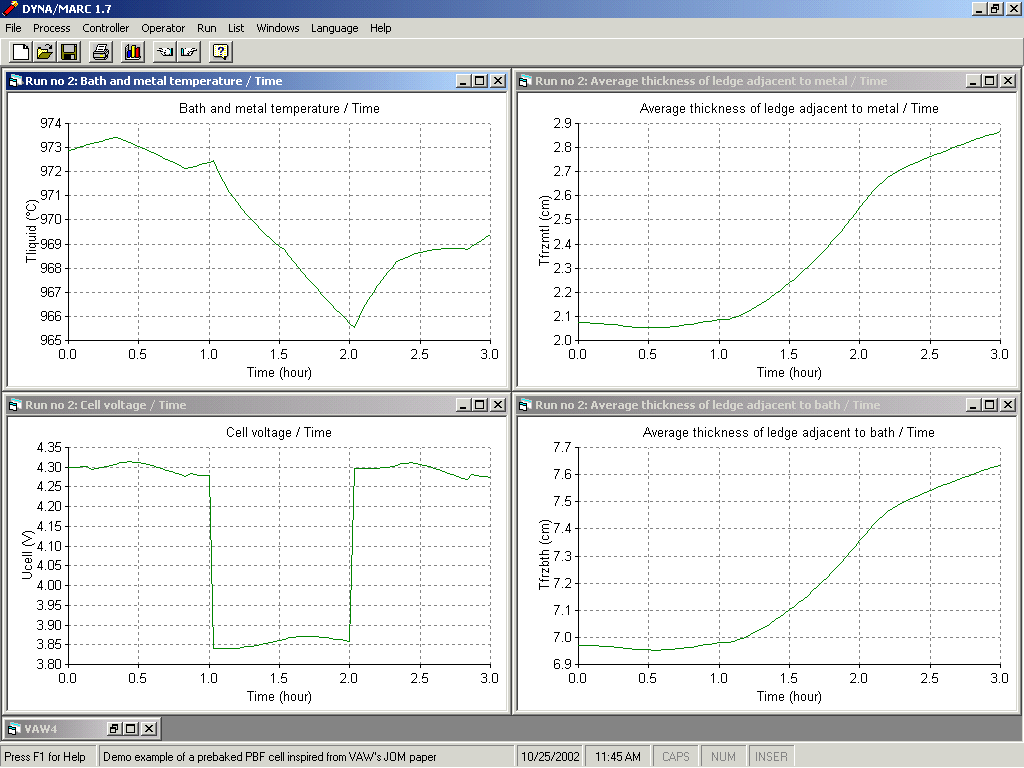
Figure 4: Example of power modulation analysis using Dyna/Marc 1.7